Perioral Dermatitis vs. Seborrheic Dermatitis: Key Differences
Key Takeaways
- Perioral Dermatitis typically appears as red bumps around the mouth, while Seborrheic Dermatitis shows as oily, scaly patches on the scalp and face.
- Common triggers include certain skincare products, environmental factors, and hormonal changes.
- Options range from over-the-counter remedies to prescription medications, depending on the severity.
- Accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans are crucial for effective management of these conditions.
Skin conditions profoundly affect millions of people worldwide, impacting not just their skin but also their confidence and daily functioning. Among these, Perioral Dermatitis and Seborrheic Dermatitis are particularly significant due to their common occurrence and the confusion often surrounding their management. This blog delves into each condition, providing a thorough understanding of their symptoms, causes, and treatment strategies.
Understanding Perioral Dermatitis
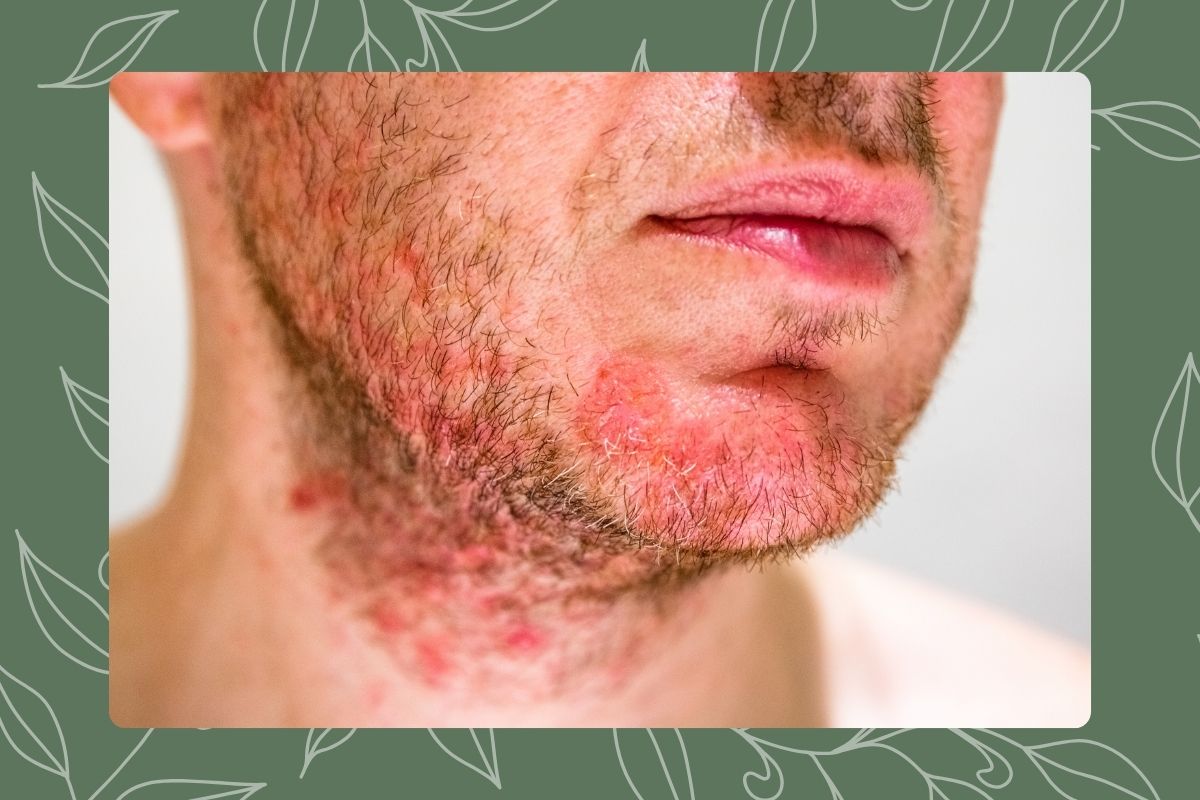
Perioral Dermatitis is an inflammatory rash that appears around the mouth and occasionally extends to the nose and eyes. Predominantly affecting young women and children, this condition presents as a series of small red bumps, which may be accompanied by scaling or itching.
Appearance and Symptoms
The rash associated with Perioral Dermatitis can vary significantly:
- Red, inflamed patches around the mouth.
- Small bumps that may fill with fluid or pus.
- Occasional peeling or flaky skin, creating a scaly appearance.
- Itching or burning sensations, especially if products that irritate the skin are used.
Common Causes and Triggers
Several factors can trigger or worsen Perioral Dermatitis, including:
- Skincare Products: Heavy face creams, petroleum jelly, or topical steroids.
- Cosmetics: Silicone-based or oil-heavy makeup products.
- Dental Products: Fluoridated toothpaste and mouthwashes.
- Environmental Factors: Changes in weather, particularly cold and dry conditions.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Periods of hormonal change such as puberty, pregnancy, or menstrual cycles.
Diagnosis
Perioral Dermatitis is diagnosed based on clinical examination. Dermatologists may also perform swab tests to exclude bacterial or fungal infections, which can appear similar.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment strategies include:
- Discontinuing the use of triggering facial products.
- Applying topical antibiotics like metronidazole or erythromycin.
- In some cases, low-dose oral antibiotics for more severe outbreaks.
- Emphasizing gentle skin care and the use of non-irritating products.
Exploring Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic Dermatitis is a long-term skin disorder affecting areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. It is marked by red skin covered with flakes and scales, often causing dandruff in adults and cradle cap in infants.
Appearance and Symptoms
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis include:
- Oily, scaly patches on the scalp, eyebrows, or beard area.
- White or yellow scales that may attach to the hair shaft and flake off.
- Red, itchy skin beneath the scales.
- In severe cases, hair loss if the scalp is heavily affected.
Common Causes and Triggers
The causes and exacerbating factors for Seborrheic Dermatitis are diverse:
- Yeast Infections: Overgrowth of the yeast Malassezia on the skin.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of similar skin conditions.
- Medical Conditions: Stress, fatigue, or other skin disorders like psoriasis.
- Environmental: Extreme weather conditions, either too hot and humid or cold and dry.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis usually involves a physical examination and patient history. In uncertain cases, a biopsy or other dermatological tests may be performed to rule out psoriasis or other dermatological diseases.
Treatment Options
Managing Seborrheic Dermatitis includes:
- Medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione.
- Topical antifungals and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and yeast proliferation.
- Regular washing with gentle cleansers to reduce oil accumulation and skin irritation.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing Perioral Dermatitis and Seborrheic Dermatitis involves more than just treating the symptoms; it requires a comprehensive approach that considers both environmental and biological factors. These conditions not only affect the skin but also the emotional well-being of those who suffer from them. By recognizing the triggers, correctly diagnosing the condition, and employing a tailored treatment strategy, individuals can effectively manage these dermatological challenges and improve their quality of life. Whether through over-the-counter solutions or prescription treatments, it is important to consult with a dermatologist to develop a care plan that addresses both the physical symptoms and the overall health of the skin. Remember, healthy skin is more than just a reflection of our physical health—it’s integral to our overall confidence and happiness.
FAQs
1. What causes Perioral Dermatitis and Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Perioral Dermatitis is often caused by the use of topical steroids, heavy skin creams, or cosmetic products that irritate the skin. Environmental factors like wind and cold weather, hormonal changes, and stress can also trigger this condition. Seborrheic Dermatitis, on the other hand, is commonly associated with an overgrowth of yeast called Malassezia on the skin, genetic factors, and environmental triggers such as stress and weather changes. It can also be exacerbated by oily skin and hormonal fluctuations.
2. How can I tell if I have Perioral Dermatitis or Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Perioral Dermatitis typically appears as a rash of red bumps around the mouth, and sometimes around the nose and eyes, which can be accompanied by scaling or itching. Seborrheic Dermatitis usually presents with oily, scaly patches on the scalp, face, and other oily areas of the body. The scales can be white or yellowish and may be accompanied by redness and itching. If you are unsure, it is best to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis.
3. Can diet affect Perioral Dermatitis or Seborrheic Dermatitis?
While there is no definitive link between diet and these skin conditions, some people find that certain foods can exacerbate their symptoms. Foods high in sugars and fats can promote inflammation and may worsen Seborrheic Dermatitis. Similarly, spicy foods or caffeinated beverages might trigger flare-ups in some individuals with Perioral Dermatitis. Keeping a food diary to track what you eat and how it affects your skin can be a useful way to determine if your diet impacts your skin condition.